- News
- City News
- bhopal News
- Renal failure deaths 3 times higher among Bhopal gas victims
Trending
This story is from December 2, 2018
Renal failure deaths 3 times higher among Bhopal gas victims
Representative image
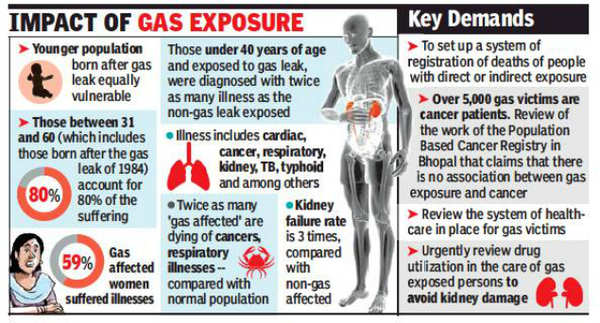
BHOPAL: More than three decades after the Bhopal gas disaster of 1984, kidney failure rate among the ‘affected’ population is three times higher than the average population. Twice as many 'gas affected' are dying of cancers, respiratory illnesses and even more are falling sick each day, says a five-year study report on status of gas victims prepared by the Bhopal-based NGO Sambhavna Trust Clinic, released here on Saturday.
The study reports 28% more deaths among gas exposed population compared to the unexposed population pointing to the fact of continuing deaths associated with Bhopal gas leak exposure.

The reported titled ‘Health and Healthcare In Gas Exposed and Unexposed Populations’ has linked data points from the gas exposed and unexposed populations on deaths in their immediate families between January 1, 2012 and March 31, 2017. “It shows that rates of deaths for causes other than accidents in exposed and unexposed populations are 63.48 and 49.32 respectively,” said Bhopal Group for Information and Action (BGIA), representative Rachna Dhingra.
Around 5.72 lakh people are registered as affected by exposure to the poisonous gas that leaked from UCIL pesticide plant killing thousands and maimed lakhs on the night of December 2 and 3 in 1984. 34 years on, dependents of the victims too are categorised to receive free healthcare.
Sambhavna Trust Clinic study focused on efforts from 2010 to 2011 to register a cohort population for studying the long-term health impact of exposure to Union Carbide's poisons, in the form of gas or contaminated ground water. The cohort population registered by the CRU at the clinic includes about 94,000 people who had exposure to Union Carbide's gas leak and water contaminated by Carbide's hazardous waste and people of similar socio-economic status without exposure to gas or contaminated water.
The only other comprehensive study on Bhopal gas victims has been by Union government’s apex research agency, the Indian Council of Medical Research. It published its technical report on death and illness caused by the Union Carbide gas disaster till 1994.
The report was based on information collected on 80,021 gas-affected and 15,391 people of similar socio-economic status without gas exposure.
A second technical ICMR report was published in 2013 based on information collected on death and disease from 1996 to 2010 indicated that these information could not be collected from 79% of the gas-affected persons and 64% persons in the unexposed control population. Reliability of the information on long-term health impact of exposure to Union Carbide's gases was challenged by activist who alleged ‘loss of cohort’ population.
The study reports 28% more deaths among gas exposed population compared to the unexposed population pointing to the fact of continuing deaths associated with Bhopal gas leak exposure.
The reported titled ‘Health and Healthcare In Gas Exposed and Unexposed Populations’ has linked data points from the gas exposed and unexposed populations on deaths in their immediate families between January 1, 2012 and March 31, 2017. “It shows that rates of deaths for causes other than accidents in exposed and unexposed populations are 63.48 and 49.32 respectively,” said Bhopal Group for Information and Action (BGIA), representative Rachna Dhingra.
Report links statistical evidence of diseases related to renal, respiratory, ocular, gastrointestinal, reproductive, neurological, immunological, psychological disorders caused by exposure to toxic gas.
Around 5.72 lakh people are registered as affected by exposure to the poisonous gas that leaked from UCIL pesticide plant killing thousands and maimed lakhs on the night of December 2 and 3 in 1984. 34 years on, dependents of the victims too are categorised to receive free healthcare.
Sambhavna Trust Clinic study focused on efforts from 2010 to 2011 to register a cohort population for studying the long-term health impact of exposure to Union Carbide's poisons, in the form of gas or contaminated ground water. The cohort population registered by the CRU at the clinic includes about 94,000 people who had exposure to Union Carbide's gas leak and water contaminated by Carbide's hazardous waste and people of similar socio-economic status without exposure to gas or contaminated water.
The only other comprehensive study on Bhopal gas victims has been by Union government’s apex research agency, the Indian Council of Medical Research. It published its technical report on death and illness caused by the Union Carbide gas disaster till 1994.
The report was based on information collected on 80,021 gas-affected and 15,391 people of similar socio-economic status without gas exposure.
A second technical ICMR report was published in 2013 based on information collected on death and disease from 1996 to 2010 indicated that these information could not be collected from 79% of the gas-affected persons and 64% persons in the unexposed control population. Reliability of the information on long-term health impact of exposure to Union Carbide's gases was challenged by activist who alleged ‘loss of cohort’ population.
End of Article
FOLLOW US ON SOCIAL MEDIA










